Inner Ear Balance (Vestibular) Disorders
Complete Care for Inner Ear Disorders
There are several types of inner ear balance disorders that can cause problems with vertigo and hearing loss to one or both of your ears. University of Chicago Medicine otolaryngologists and audiologists can help diagnose and treat your the full scope of vestibular diseases. Common inner ear balance disorders include:
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), also known as positional vertigo, is a dizzy or spinning sensation in your head, and is the most common type of vertigo.
- Meniere's disease causes episodes of vertigo, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), ear pressure/fullness and hearing loss.
- Labyrinthitis and vestibular neuritis occurs when the hearing and balance nerves become inflamed, resulting in sudden hearing loss, balance problems and vertigo.
- Superior semicircular canal dehiscence (SSCD) is a rare condition where a patient has a loss or absence of the bone that covers your superior semicircular canal. With SSCD, you may have a variety of unusual symptoms, such as pressure- or sound-induced vertigo, hearing loss, ear pressure, or even hearing your own breathing and blinking.
Diagnosing Inner Ear Balance (Vestibular) Disorders
When diagnosing vestibular disorders, our audiologists may perform a videonystagmography (VNG), electrocochleography (ECoG) and/or vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials (VEMPs) to determine the functionality of your inner ear balance system.
Vestibular Evaluations
Vestibular testing is performed if you are experiencing dizziness, vertigo or imbalance. Depending on your symptoms, we may do several different tests during your visit to determine how well your vestibular system is working. Some of these tests are irritating and may temporarily exacerbate your symptoms of dizziness/vertigo, so we recommend you have a friend or family member accompany you to your appointment and help get you home afterward.
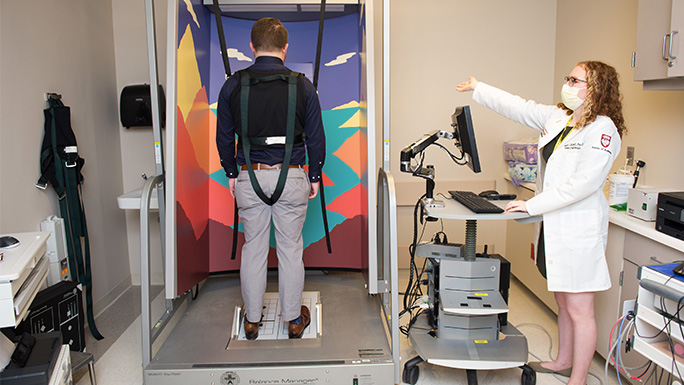
Computerized Dynamic Posturagraphy
Computerized dynamic posturography is used to objectively quantify and differentiate among three sensory inputs; the vestibular (inner ear system), somatosenory (feet, ankles, joints) and vision (eyes). When all three sensory inputs are working together, you will have proper balance. When one or more of the senses are not cooperating, you will experience imbalance or dizziness.
Computerized dynamic posturography cannot diagnose the source of your dizziness on its own, but it can be used in conjunction with other clinical test to help localize and categorize the sensory system or systems causing your dizziness or balance.
During a computerized dynamic posturography, you will be standing on a platform while wearing a safety harness, and you will remove your shoes so you have full access to the somatosensory input from your feet. We will administer a series of tests to measure how well you can maintain your balance under different conditions.
During VNG testing, you will be wearing video goggles to record your eye movements. In part one, you will be asked to follow moving dots on the wall with your eyes. The second part involves moving your head and body into different positions, and in the last part, we test your caloric reflex. In part three we will put cool and warm air into the ear canal for one minute and measure the resulting nystagmus or eye movements. It is normal to feel dizzy during this test, but this feeling should subsides quickly.
Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential (VEMP)
For VEMP testing, electrodes will be placed on your forehead, under your eyes, along the sides of your neck and on your clavicle. Once those are secured, headphones will be inserted into your ear canal and a loud clicking noise is play in one ear while you look up or turn and look over your shoulder.
Video Head Impulse Testing (vHIT)
If you are having vHIT testing, you will wear special goggles to track your eye movements. You will be asked to focus on a target in front of you and the audiologist will make sudden movements of your head in certain directions to stimulate the various balance canals of your inner ear.
Treatment for Inner Ear Disorders
Our expert team collaborates with other University of Chicago Medicine and community-based specialists in neurology, psychiatry, physical therapy and occupational therapy so that, together, we can provide our patients with high-quality care and improved outcomes.
Schedule an Appointment

Schedule an Appointment Online
Learn more about our specialists and schedule an appointment directly through our online scheduling portal.

Schedule a Video Visit
Save time by skipping the trip to the doctor's office and video conference with your provider instead. Video visits are a secure, quick, and convenient way to connect with your doctor and other members of your care team.
Request an Appointment
Don't have time right now? Submit an appointment request form and we'll call you back within two days to schedule an appointment.
